Can You Read a File Into an Unordered Map
Introduction to C++ unordered_map
In C++, Unordered maps are considered associative containers, which helps store elements generated by the key-value and mapped value combination. This function permits the fast retrieval of separate elements that are based on their keys. Here, the cardinal value is mainly used to notice the item uniquely, and the mapped value is considered an object with the content linked to this central. There may exist differences in the types of key-value and mapped value. Let us come across more about the unordered map in the following sections. In this topic, we are going to learn virtually C++ unordered_map.
Definition
Below is the definition of unordered maps in C++
template< class K , class T,class Hash = hash<K>,
classPred = equal_to<K>,
classAlloc = allocator< pair<constK,T>>
>classunordered_map;
The parameters are:
- Grand, which is the key type.
- T, which is then mapped value type
- Hash, a type of unary function object that gets an object of key blazon equally a parameter and returns a specific value of size t.
- Pred, this is a binary predicate.
- Alloc, which is the blazon of object of the allocator.
T may be replaced past any data type containing a user-divers type.
Member Types of C++ unordered_map
Below are the member types that can be used by member functions as arguments or return types.
| Member types | Clarification |
| key_type | Key; Parameter 1 used for the template |
| mapped_type | T; Parameter 2 used for the template |
| hasher | Default value: hash<key_type> ;Parameter 3 used for the template |
| key_equal | Default value: equal_to<key_type>); Parameter 4 used for the template |
| allocator_type | Alloc; Parameter 5 used for the template |
| value_type | pair<constkey_type,mapped_type> |
| reference | value_type& |
| const_reference | constvalue_type& |
| difference_type | ptrdiff_t |
| size_type | size_t |
| pointer | allocator_traits<Alloc>::arrow |
| iterator | A forrard iterator for the value_type value_type |
| local_iterator | A forwards iterator for the value_type |
| const_iterator | A forward iterator for the constvalue_type value_type |
| const_pointer | allocator_traits<Alloc>::const_pointer |
| const_local_iterator | A forwards iterator for the constvalue_type |
Constructors
The following are the constructors of the c++ unordered map.
- unordered_map::unordered_mapdefault constructor
An empty unordered_map will be constructed with a number of elements as null.
- unordered_map::unordered_mapcopy constructor
An unordered_map will be constructed with each element's copy. Thus, these elements volition exist already on the existing map.
- unordered_map::unordered_mapmove constructor
An unordered_map volition be constructed with the content present in another map using the semantics motion.
- unordered_map::unordered_maprange constructor
An unordered_map will be constructed with items in the range from first to last.
- unordered_map::unordered_mapinitializer_list constructor
An unordered_map will be synthetic from the initializer list.
Methods on unordered_map
In an unordered map of C++, a plethora of functions is nowadays. The most useful amidst them are = operator, [] operator, iterator begin and end, size and empty for capacity, lookup notice and count, modification- insert and erase.
How unordered_map function work in C++?
In unordered_map, the elements are not sorted initially based on any particular guild with respect to key values or mapped values. Instead, it is simply structured into buckets bailiwick to the hash values to allow fast admission to distinct items directly past their values of keys.
Moreover, the containers of the unordered maps are faster than the containers of the map to access singled-out elements based on their primal, fifty-fifty though they are ordinarily less efficient for iteration based on range through their elements subset.
These unordered maps implement the operator [], besides known as a directly access operator that permits the mapped value straight admission using its central value.
Let us understand more most the unordered map using the sample lawmaking.
- Ascertain the unordered_map with some elements
unordered_map<char, int>mp = {
{'H', 21} ,
{'I', 52} ,
{'J', 36} ,
{'K', 47} ,
{'50', 54}
};
- Define an Iterator itr
auto itr = mp.discover('L');
- print the values based on the requirement
Examples of C++ unordered_map
To understand more about the unordered map, let us work with some sample programs.
Example #ane
C++ program to find a detail element in an unordered map.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
//use the namespace as std
using namespace std;
//code for unordered_map begins here
int main(void)
{
//define the unordered_map
unordered_map<char, int>mp = {
{'H', 21} ,
{'I', 52} ,
{'J', 36} ,
{'K', 47} ,
{'L', 54}
};
//Iterator itr
motorcar itr = mp.notice('L');
//print the iterator than links to the graphic symbol 'L'
cout<< "Iterator links to " <<itr->first
<<" is " <<itr->second <<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
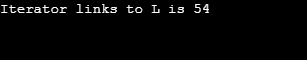
Commencement, use the namespace as std. And then, define the unordered_map with elements {'H', 21} ,{'I', 52} , {'J', 36} , {'K', 47} , {'Fifty', 54. In one case the elements are defined, utilise the iterator to detect the element 50 and fundamental that is linked to that particular character. On executing the code, the value linked to L will be printed.
Example #2
C++ program to print all the elements in an unordered map.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <unordered_map>
//utilise the namespace equally std
using namespace std;
//code for unordered_map begins here
int principal()
{
unordered_map<int, char> mp1;
unordered_map<int, char>::iterator crs;
mp1[one] = 'a';
mp1[2] = 'b';
mp1[3] = 'c';
mp1[4] = 'd';
mp1[5] = 'e';
mp1[6] = 'f';
mp1[7] = 'g';
mp1[eight] = 'h';
cout<< "Key value\t corresponding element" <<endl;
for (crs = mp1.begin(); crs != mp1.end(); crs++)
{
cout<<crs->outset;
cout<< '\t' <<crs->2d << '\n'
<<endl;
}
}
Output:
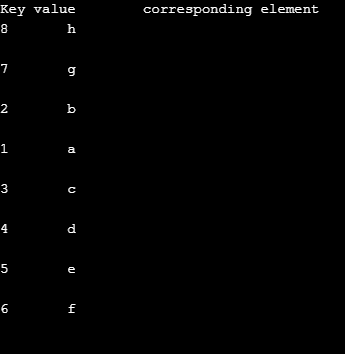
In this program, also, first, utilize the namespace as std. And so, ascertain the unordered_map with elements {and an iterator. In one case the elements are defined, use the iterator to discover all the elements and key that is linked to that particular character. It is done with the help of using begin() and end () functions. Finally, on executing the code, all the elements and corresponding values will be printed.
Determination
Unordered maps are the associative containers that assist in storing elements generated by the key-value and mapped value combination. In this article, unlike aspects such as definition, constructors, methods, working, and examples of the unordered map are explained in detail.
Recommended Manufactures
This is a guide to C++ unordered_map. Here we discuss How the unordered_map function work in C++ and Examples forth with the codes and outputs. Y'all may as well have a wait at the post-obit articles to learn more than –
- C++ String Copy
- Type Casting in C++
- C++ setprecision
- C++ Listing
Source: https://www.educba.com/c-plus-plus-unordered_map/
0 Response to "Can You Read a File Into an Unordered Map"
Publicar un comentario